We will name below some cases in which it clearly shows the abuse of the use of our personal information in the networks, are just some examples where it is left in evidence to what extent studies, application and use in favor of society are necessary of cryptographic knowledge. The Electronic Privacy Information Center (“EPIC”) is a public interest research center located in Washington, D.C. EPIC focuses on emerging issues of privacy and civil liberties and is a prominent consumer advocate with the FTC (Federal Trade Commission). This body revealed and denounced before US courts the use of the so-called “store tracking algorithm” that would allow Google to identify the purchases of people inside and outside the network. According to the complaint reported by EFIC to the FTC, since Google introduced its “store sales management” program in May, it began a massive tracking of transactions made with credit cards outside the Internet, which can reveal a large amount of personal and potentially sensitive information from users.
“This data reveals sensitive information about consumers’ purchases, their health and their privacy, and according to Google, it can track 70% of transactions made with credit and debit cards in the United States.” Mention the document.

In India, citizens lose their right to privacy because from New Delhi they have made the use of Aadhaar mandatory for access and provision of essential private services. Aadhaar is an identification number issued by the government of India that collects personal data (name, phone, address …) and biometrics (including the fingerprint and iris) of the residents of this country, the government of India intends that in the future all bank accounts in the country are linked to Aadhaar identification numbers. Aadhaar is probably the largest biometric identification system in the world, linking its accounts to a single ID and creating a network of data points that could be used to profile or track people. The fact that there is a base with all this information represents, according to some privacy advocates, a threat to citizens, to the extent that it grants enormous power to the current government, successive or even malicious actors. And the law that regulates the data network explicitly denies citizens the right to go to court to request damages for the disclosure of their personal data. Only the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI), the agency in charge of Aadhaar, can sue the government in
The Supreme Court of India rules that privacy is a fundamental right and gives new arguments to the critics of the Aadhaar state database.

An international group of researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Rutgers University, both in the US UU., Together with colleagues of the University of Aarhus, in Denmark, have carried out a study to test the effectiveness of the privacy of the users of credit cards in a world dominated by the massive exchange of data. They have analyzed data from more than one million anonymous people and have shown that, with only four data that indicate the space and time of various transactions made with a credit card, you can identify 90% of the individuals in a database . The scientists of this study, led by Yves-Alexandre de Montjoye, a researcher at MIT’s Media Lab, observed for three months the data generated by the financial transactions of 1.1 million people, made with credit cards, who lived inside an unidentified country of the Organization for Cooperation and Economic Development ( OCDE ).
Among the findings, the team notes that women and people with higher incomes are easier to identify through this method because they have distinctive patterns in the way they divide their time between the stores they visit. The results, the authors add, indicate that it is necessary to improve anonymous data protection technologies to increase security.

“Cryptography is the last form of nonviolent direct action, even though States with nuclear weapons can exercise unlimited violence against millions of individuals, cryptography means that a State, even exercising unlimited violence, can not violate the intention of Individuals keep their secrets out of their control, good cryptography can withstand the unlimited application of violence “Julián Assange.
The Bitcoin protocol uses the algorithm ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm) for the creation of private and public keys. The main advantage of elliptic curve cryptography is the possibility of creating smaller keys, thus reducing storage and transmission requirements. A key based on elliptic curve cryptography can give the same level of security with a 256-bit key as an RSA algorithm with a 2048-bit key. The ECDSA algorithm creates 256-bit-long keys coded with Bitcoin’s Base58 positional numbering system that gives 44-digit keys without including the version number or control digits. A key with RSA would need 350 digits. The main reason for using elliptic curve cryptography was thus to facilitate the handling of the public addresses of the Bitcoin protocol.
Bitcoin arrived in 2009 as an alternative currency solution that can be used to make transactions between two parties without the need for a reliable third party, this is based on the specific rules when incorporating data into the network, data can not enter in conflict with some other data that is in the database (consistent), it is only of annexation (immutable) and the data is blocked to an owner (property) is replicable and accessible and all those involved in the transactions are in agreement with the state of things in the database (canonical) without a central part (de-centralized). But what level of Privacy can Bitcoin offer us in our transactions? One of the tools that exist for tracking transactions with blockchain technology is the Wallet Explorer. This can show all the history of a flow of funds in the blockchain.
All the information that we want to verify about an address, transaction or block is at our disposal thanks to it.
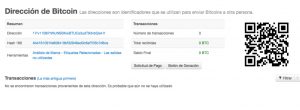
It will show the addresses that have sent bitcoins to the address that we want to consult, balances and an ordered history of transactions.
This way every time we make a transaction, indirectly we are revealing data about our funds. I want my neighbor, my doctor or my son’s private teacher, to obtain the information of what funds are available to me? You can also get a record of all my transactions, and if you really have an interest you can figure out what and where I have bought with my Bitcoin wallet. Bitcoin solves most of the problems we have derived from the use (almost by conviction) of fiduciary currencies, controlled and in many cases manipulated by the states that subject society to a constant loss of purchasing power. But like all new technology requires of advances, improvements or modifications since in regard to privacy, does not meet the conditions to offer the consumer the desired level of privacy.
BitcoinPrivate is a Bitcoin fork that adds armored addresses (Z-Address) to Bitcoin.
BitcoinPrivate by using the zk-SNARKs protocol, a novel form of zero-knowledge cryptography guarantees privacy. The strong privacy guarantee of BitcoinPrivate stems from the fact that transactions shielded in BitcoinPrivate can be fully encrypted in the blockchain, and can still be verified as valid under network consensus rules by using zk- tests. SNARK. BitcoinPrivate private transactions with zk-SNARK protect the Issuer + Receiver + Sent Quantity, as well as provide the largest anonymity set of any currency ever created.
The acronym zk-SNARK means “Concise non-interactive argument of zero knowledge”, and refers to a test construction where one can prove possession of certain information, eg. a secret key, without revealing that information, and without any interaction between the tester and the verifier.
The “zero knowledge” tests allow one of the parties (the tester) to prove to another (the verifier) that a statement is true, without disclosing any information beyond the validity of the statement itself. For example, given the hash of a random number, the tester could convince the tester that there is indeed a number with this hash value, without revealing what it is.
In a “knowledge test” of zero knowledge, the tester can convince the tester not only that the number exists, but that they actually know that number, again, without revealing any information about the number.
These days we have been able to see in social networks as known actors in the world of cryptocurrencies have come out in defense of the idea that PRIVACY is a necessary right that we are losing and that we must work to be able to return that right to society in all aspects.
Not only the charismatic John McAfee great defender and expert in the crytocurrencie world.

We have also been able to read to Vitalik Buterin the young creative genius of Etherum, talking about the need to work for privacy, since in the physical space it is quite inevitable to try to get it on the internet.
I made a comment yesterday in a thread about how my opinions about privacy have changed in recent years (I’m more in favor of privacy now), and they encouraged me to push it. Here you have:
I am considerably more in favor of privacy than a few years ago. A few years ago, my position was closer than “in a well-functioning society everyone is likely to see everything, the value of privacy technology for ordinary people is to let them buy grass, put beds so that people can sleep in offices, and otherwise bypass silly regulations, and maintain a healthy balance of power, because even if more transparency is good, the government only has the eye that sees everything and everyone else is in the dark would give too much power to the goverment.
Things that changed my mind and made me believe that even in a perfectly egalitarian and fair hypothetical society, people who have some privacy are a good idea, they include:
Reading the literature of Robin Hanson and others on signage, and seeing how great a portion of our lives still is. Basically, I see privacy as a way to prevent signaling concerns from covering all of our activity, and to create areas in which we are free to optimize our own happiness and our own happiness, and not what other people think of us. Have a deeper understanding of the ways in which it is possible to make other people’s lives shit, even as a private citizen respectful of the law, and realize that privacy is an important self-defense tool for those situations. Understanding more deeply that “people” is not always virtuous, and that social pressure as a mechanism to influence people’s behavior does not always lead to results that I approve (see: recent series of internet mobs that lead people fired by political opinions) When realizing how bad the traditional media are now, what makes me better understand the desire of people to protect themselves from them. Massive surveillance is problematic because I do not trust governments and large corporations to have interests aligned with us, and creates centralized data collection points that could be pirated, which leads everyone to obtain that data even if that was never the original intention. That said, in physical space it is quite inevitable, so at least we should work hard to make the Internet a place that preserves privacy.
The answer to the question of the title of the article will continue to imply a struggle of forces and resources, in that struggle the use of physical force is not required, but the use of our intellectual force, we release our privacy, it is a human right and not We can lose it.
If you are interested in learning more about BitcoinPrivate and your community, join in your social networks.